1) What is Perinatal Hospice?
Kliegman:
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics,
18th ed.
Copyright ©
2007 Saunders, An
Imprint of Elsevier
Chapter 694 – Disorders Involving Transmembrane Receptors
William A. Horton Jacqueline T. Hecht
ACHONDROPLASIA
GROUP
THE
achondroplasia group represents a substantial percentage of patients with
chondrodysplasias and contains
thanatophoric
dysplasia (TD), the most common lethal chondrodysplasia with an incidence
of 1/35,000 births;
achondroplasia, the most common nonlethal chondrodysplasia with an incidence
of 1/15,000 to 1/40,000 births; and hypochondroplasia. All three have
mutations in a small number of locations in the FGFR3 gene. There is
a strong correlation between the mutation site and the clinical phenotype.
Websites
THANATOPHORIC
DYSPLASIA.
TD presents
before or at birth. In the former situation, ultrasonographic examination in
midgestation or later reveals a large head and very short limbs; the pregnancy
is often accompanied by polyhydramnios and premature delivery. Very short limbs,
short neck, long narrow thorax, and large head with midfacial hypoplasia
dominate the clinical phenotype at birth . The cloverleaf skull deformity known
as kleeblattschödel is sometimes found. Newborns have severe respiratory
distress because of their small thorax. Although this distress can be treated by
intense respiratory care, the long-term prognosis is poor.
|
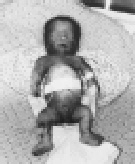 |
Figure 694-1
Stillborn infant with
thanatophoric
dysplasia. Limbs are very short, with upper limbs extending only two
thirds of the way down the abdomen. The chest is narrow, exaggerating
the protuberance of the abdomen. The head is relatively large.
|
  |
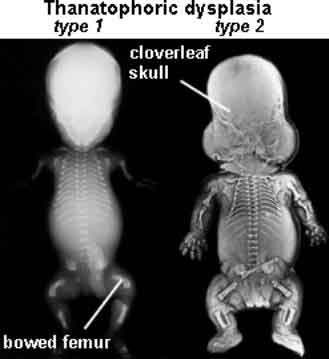
Skeletal radiographs
distinguish two slightly different forms called TD I and TD II. In the more
common TD I, radiographs show large calvariae with a small cranial base, marked
thinning and flattening of vertebral bodies visualized best on lateral view,
very short ribs, severe hypoplasia of pelvic bones, and very short and bowed
tubular bones with flared metaphyses . The femurs are curved and shaped like a
telephone receiver. TD II differs mainly in that there are longer and straighter
femurs.
|
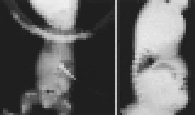 |
Figure 694-2
A, Neonatal radiograph of a child
with thanatophoric
dysplasia. Note medial acetabular spus (black arrow),
hypoplastic iliac bones, bowed femora with rounded protrusion of
proximal femurs, hypoplastic thorax, and wafer-thin vertebral bodies.
B, Lateral radiograph of the thoracolumbar spine in
thanatophoric
dysplasia, showing marked vertebral flattening and short ribs.
Ossification defect of the central portion of the vertebral bodies is
present. |
  |
The TD II clinical
phenotype is associated with mutations that map to codon 650 of FGFR 3,
causing the substitution of a glutamic acid for the lysine. This activates the
tyrosine kinase activity of a receptor that transmits signals to intracellular
pathways. Mutation of lysine 650 to methionine is associated with a clinical
phenotype intermediate between TD and achondroplasia referred to as severe
achondroplasia with developmental delay and acanthosis nigricans or SADDAN.
Mutations of the TD I phenotype map mainly to two regions in the extracellular
domain of the receptor, where they substitute cysteine residues for other amino
acids. Free cysteine residues are thought to form disulfide bonds promoting
dimerization of receptor molecules, leading to activation and signal
transmission.
TD I and TD II
represent new mutations to normal parents. The recurrence risk is low. Because
the mutated codons in TD are mutable for unknown reasons and because of the
theoretical risk of germ cell mosaicism, parents are offered prenatal diagnosis
for subsequent pregnancies.
1) What is Perinatal Hospice?
Gabbe:
Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies, 5th
ed.
Copyright
©
2007 Churchill Livingstone, An Imprint of Elsevier
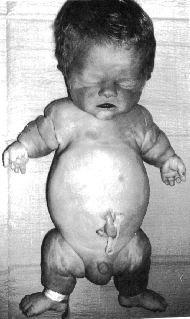
Thanatophoric dysplasia is the most
common lethal skeletal dysplasia. In this condition, there is extreme shortening
of the long bones. The femur is often bowed, resembling a telephone receiver .
The fetus has a small, narrow chest that results in lethal pulmonary hypoplasia
. The abdomen and head appear relatively enlarged. In about one of six cases,
the head has a cloverleaf shape. Hydrocephalus and polyhydramnios are common.
This Webpage
was created for a workshop held at Saint Andrew's Abbey, Valyermo, California in
1990....x.... ’ “”.



